Technical Features
Cross flow nebulizers have been available for many years and the design is extremely simple. A nebulizer gas orifice is positioned at 90 degrees to sample orifice through which sample is pumped. Argon gas exiting the gas orifice shears the liquid, generating a fine aerosol. Typically, cross flow nebulizers use a mixture of platinum, alumina or sapphire for the gas and sample orifices which can lead to increased background for some elements, and some limitations on chemical compatibility.
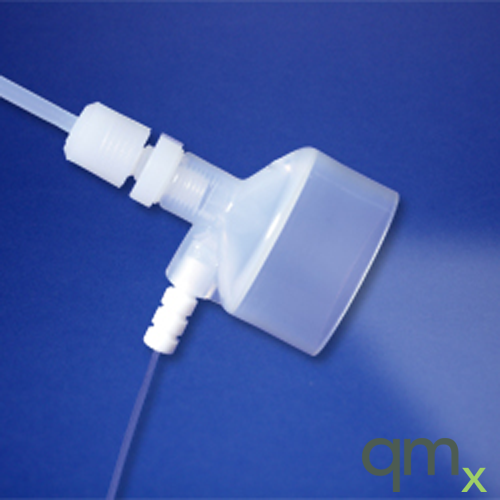
The Savillex X-Flow cross flow nebulizer is unique in that both orifices are moulded from high purity virgin PFA, that is chemically inert and offers several advantages other materials used for cross flow nebulizers.
An optional make up gas port which can be used to add O2 for organics analysis, or when it is required to operate at higher total gas flows (>1L/min) while keeping the nebulizer gas flow at the optimum flow of approx. 1L/min. The sample uptake line connector which is a zero dead volume fitting that keeps washout time to a minimum since there is no dead space in the sample uptake path to be washed out.
Nebulizer gas and make up gas fittings accept standard 4mm OD tubing. The nebulizer gas orifice is 0.5mm that means it is virtually impossible to clog and even the highest salt content and high particulate content samples can be aspirated. Typically, the X-Flow is used with an 400µl/min uptake line with ICP-MS and with the 1000µl/min uptake line with ICP-OES, however the requirement for a Scott-type chamber limits its applicability to ICP-OES since most ICP-OES instruments are used with a cyclonic chamber. The 100µl/min uptake line is used with microvolume samples.
The available sample uptake lines of the X-Flow are as follows:
| Free aspiration uptake rate (µl/min) | Inner Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 0.38 |
| 400 | 0.51 |
| 1000 | 0.76 |
Performance
Due to the higher efficiency of the Savillex C-Flow nebulizer, the sensitivity of the X-Flow with 400µl/min uptake line is comparable (actually about 10-20% lower) to a C-Flow 200, although the X-Flow has a slightly lower oxide ratio in ICP-MS.
In comparison with a conventional glass nebulizer, the X-Flow has similar efficiency. The table below shows ICP-MS data comparing the X-Flow with a 400µl/min uptake line, with a GE Micromist (400µl/min version). Both nebulizers were pumped. Data was acquired on an Agilent 7700x ICP-MS. Sensitivity was generally similar though the X-Flow had a lower random background. Oxides were slightly lower with the X-Flow while doubly charged was slightly higher.
Comparison of an X-Flow (400µl/min uptake line) with a GE Micromist 400µl/min version. Data acquired on an Agilent 7700x ICP-MS:
| 7amu | 89amu | 205amu | Background | CeO (%) | Ce++ (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-Flow | 57104 | 28374 | 327241 | 0.2 | 0.82 | 0.92 |
| GE MicroMist | 45820 | 311864 | 274513 | 1.3 | 0.91 | 0.75 |
Comparing other properties of the two nebulizers: the X-Flow can be used only with a Scott-type double pass chamber, while the Micromist can be used with both Scott-type and cyclonic. The X-Flow has an integrated end cap for Scott type chambers while the Micromist requires a separate end cap. The X-Flow is unbreakable, is HF resistant, has lower background for boron (the Micromist is made from borosilicate glass), and has better tolerance to very high salt samples and to high levels of suspended particulates. Finally, the X-Flow has lower dead volume and so is capable of higher sample throughput.
- Nebulizer - Cross Flow
- Nebulizer
- 400µl/min